Home » Tesamorelin vs Other GHRH Peptides: Key Differences for Research
As peptide research continues to evolve, scientists often compare compounds within the same category to better understand their mechanisms and research value. Tesamorelin is frequently evaluated alongside other growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) peptides due to its distinct structure, stability, and signaling behavior.
While all GHRH peptides aim to stimulate endogenous growth hormone release, they are not identical. Differences in molecular design, duration of action, and downstream effects make Tesamorelin stand out in many research settings. Understanding these differences helps researchers choose the most appropriate compound for their specific study goals.
GHRH peptides function by binding to receptors in the pituitary gland, triggering the release of growth hormone in a pulsatile manner. This approach preserves natural endocrine feedback loops and allows for more physiologically relevant observations compared to direct growth hormone administration.
However, not all GHRH peptides interact with these receptors in the same way. Variations in amino acid sequences can influence receptor affinity, metabolic stability, and the overall consistency of hormone release.
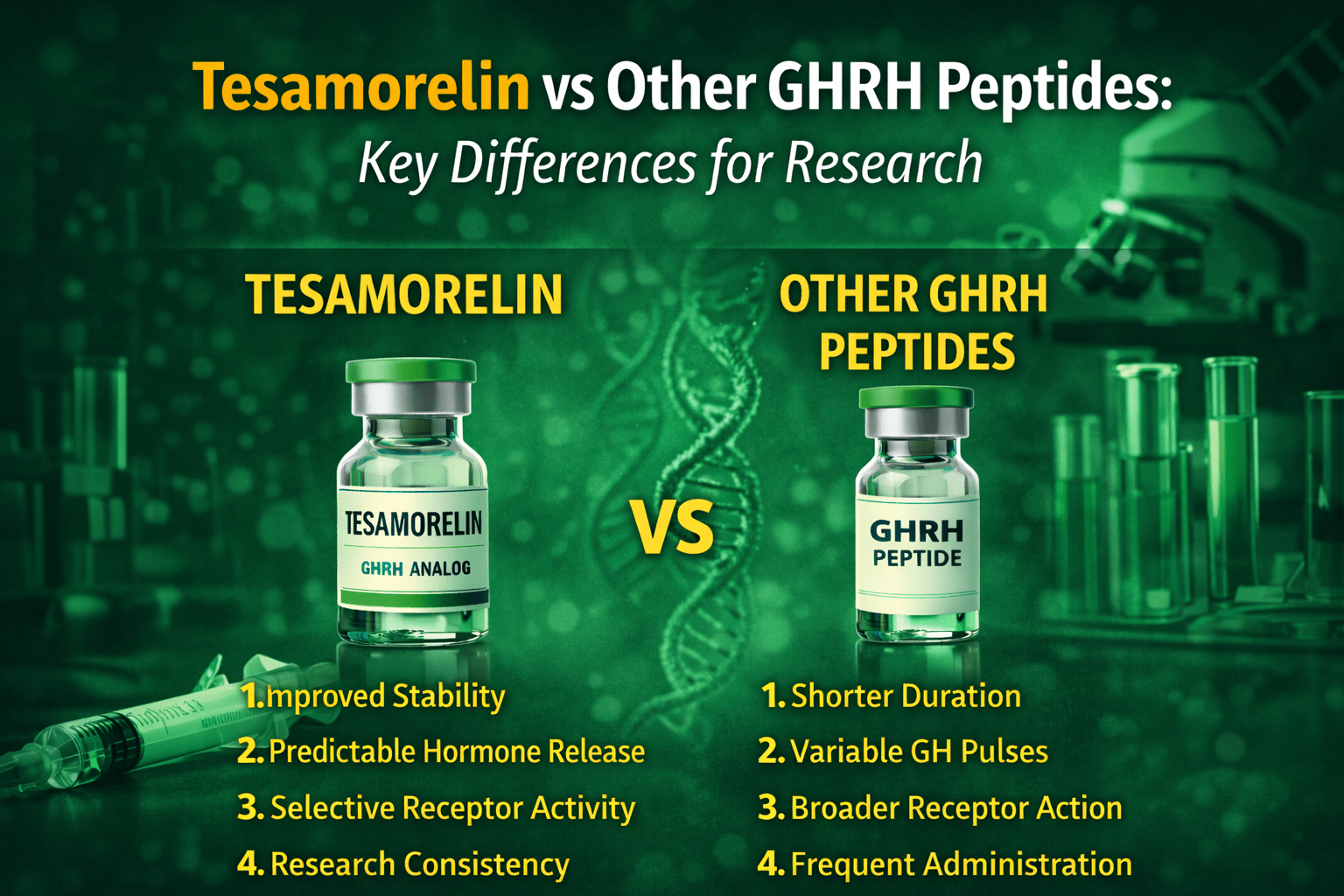
Tesamorelin was specifically engineered to improve stability and prolong activity compared to earlier GHRH analogs. Its modified structure allows it to resist rapid enzymatic breakdown, resulting in a more sustained and predictable stimulation of growth hormone release.
This enhanced stability is one of the primary reasons researchers favor Tesamorelin in long-term or repeat-dose studies. More consistent signaling allows for clearer data collection and improved reproducibility across research models.
Short-acting GHRH peptides may stimulate growth hormone release but often require more frequent administration in research settings. Their rapid breakdown can lead to variability in hormone levels, making long-term outcome measurement more challenging.
In contrast, Tesamorelin’s extended activity allows researchers to observe hormonal effects over a longer window, reducing variability and enhancing study efficiency.
Another critical comparison point is how different GHRH peptides influence insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). Growth hormone stimulates IGF-1 production in the liver, which plays a key role in cellular growth, repair, and metabolic regulation.
Tesamorelin-driven growth hormone release is often studied for its balanced effect on IGF-1 levels, allowing researchers to examine anabolic signaling without excessive or abrupt hormonal spikes.
Among GHRH peptides, Tesamorelin continues to stand out due to its engineered stability, targeted receptor activity, and reliable growth hormone stimulation. These qualities make it especially valuable for researchers seeking controlled, physiologically relevant insights into hormone-driven processes.
As peptide science advances, Tesamorelin remains a benchmark compound for comparing GHRH peptide performance and understanding growth hormone signaling at a deeper level.
Midwest Peptide supplies third-party tested research compounds with verified purity and identity. Based in the Midwest, we support academic and professional research nationwide with fast shipping, transparent lab reports, and consistent quality. Dependable materials.