Home » GLP-2 TRZ Explained: Understanding GLP-2 Pathways in Research Models
GLP-2 TRZ is a research compound derived from the GLP-2 peptide family that has gained attention in laboratory settings for its role in intestinal and gastrointestinal signaling pathways. Researchers studying GLP-TRZ focus on how GLP-2–related mechanisms influence cellular growth, nutrient absorption, and gut barrier integrity in controlled research models. This article provides an educational overview of GLP-2 TRZ and how it is examined in non-clinical research environments.
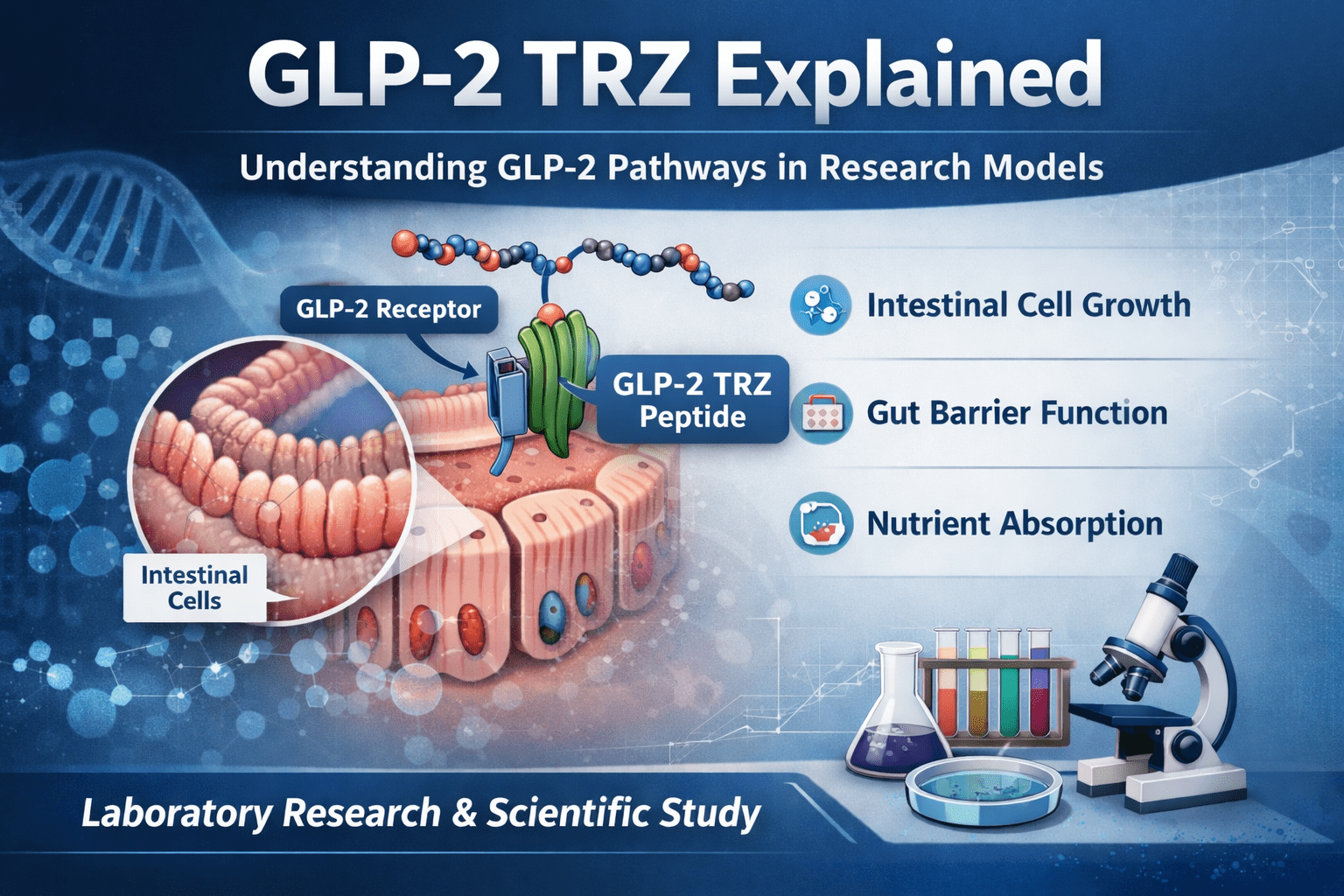
GLP-2 TRZ is a GLP-2–based research peptide designed to interact with glucagon-like peptide receptors associated with intestinal function. Unlike GLP compounds studied primarily for metabolic signaling, GLP-2–focused peptides are examined for their effects within the gastrointestinal system. GLP-2 TRZ is used in research to better understand how GLP-2 pathways regulate intestinal structure and function at the cellular level.
GLP-2 is a naturally occurring peptide hormone involved in signaling processes within the digestive tract. In research models, GLP-2 activity is associated with intestinal epithelial growth, mucosal maintenance, and nutrient transport. Scientists study GLP-2 pathways to gain insight into how the gut adapts to stress, injury, or changes in nutrient availability.
GLP-2 TRZ builds on this foundation by allowing researchers to observe GLP-2–related signaling in a more targeted and controlled way. These studies help clarify how receptor activation influences downstream cellular responses within intestinal tissues.
Research involving GLP-2 TRZ typically takes place in preclinical settings, including in-vitro and animal-based models. These studies are designed to observe how GLP-2 TRZ interacts with GLP-2 receptors and how those interactions affect intestinal cells and tissues over time.
While many GLP-based compounds are studied for metabolic or systemic signaling, GLP-TRZ is primarily researched for its localized effects within the gastrointestinal system. This distinction is important for researchers selecting compounds based on specific study goals.
GLP-2 TRZ is often discussed separately from multi-pathway GLP compounds because its research focus remains centered on gut-related biological processes rather than whole-body metabolic regulation. This makes it particularly relevant for studies centered on intestinal physiology.
Understanding GLP-2 signaling pathways provides researchers with valuable insight into how the gastrointestinal system maintains balance and adapts to changing conditions. GLP-2 TRZ offers a tool for studying these mechanisms in greater detail, helping to refine current models of intestinal biology.
Ongoing research contributes to a broader understanding of peptide signaling and supports the development of more accurate experimental frameworks in gastrointestinal science.
Current studies involving GLP-2 TRZ continue to explore receptor dynamics, signaling efficiency, and tissue-specific responses. As research methods evolve, GLP-TRZ remains a point of interest for scientists examining GLP-2–mediated pathways and their role in intestinal research models.
By focusing on controlled laboratory environments, researchers can better isolate variables and deepen their understanding of GLP-2–related biological processes without confounding external factors.
This content is intended for educational purposes only and reflects ongoing scientific research. GLP-2 TRZ is referenced exclusively in a research context.
Midwest Peptide supplies third-party tested research compounds with verified purity and identity. Based in the Midwest, we support academic and professional research nationwide with fast shipping, transparent lab reports, and consistent quality. Dependable materials.